ACR Criteria 1990
Widespread pain in combination with tenderness in 11 or more of the 18 specific tender point sites – so called tender points are defined as the main symptoms according by the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and were presented as the fibromyalgia diagnostic criteria in 1990; see the excerpt → diagnostic criteria of fibromyalgia 1990 (pdf file, one page) or one can download the full publication of the Multicenter Criteria Committee: Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, Bennett RM, Bombardier C, Goldenberg DL, et al.: The American College of Rheumatology 1990 Criteria for Classification of Fibromyalgia (pdf file, 14 pages, 4.1 MB).
I. Generalized Pain
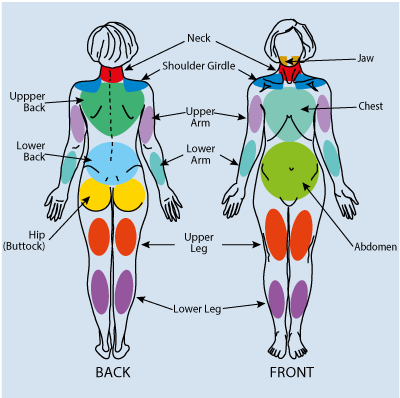
Definition. Pain is considered widespread when all of the following are present: pain in the left side of the body, pain in the right side of the body, pain above the waist, and pain below the waist. In addition, axial skeletal pain (cervical spine or anterior chest or thoracic spine or low back) must be present. In this definition, shoulder and buttock pain is considered as pain for each involved side. "Low back" pain is considered lower segment pain.
II. Tender Points
Pain in 11 or more of the 18 specific tender point sites
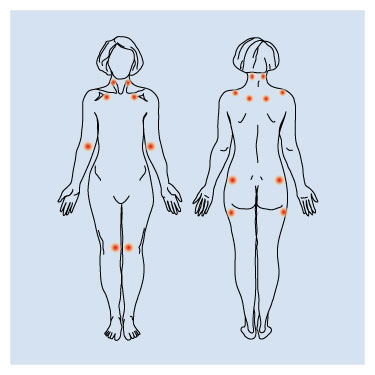
(9 symmetric pairs of tender points) examined by making a pressure by thumb or index finger. Locality of tender points proposed by ACR is as follows:
- Occiput – bilateral, at the suboccipital muscle insertions;
- Low cervical – bilateral, at the anterior aspects of the intertransverse spaces at C5-C7;
- Trapezius – bilateral, at the midpoint of the upper border;
- Supraspinatus – bilateral, at origins, above the scapula spine near the medial border;
- Second rib – bilateral, at the second costochondral junctions, just lateral to the junctions on upper surfaces;
- Lateral epicondyle – bilateral, 2 cm distal to the epicondyles;
- Gluteal – bilateral, in upper outer quadrants of buttocks in anterior fold of muscle;
- Greater trochanter – bilateral, posterior to the trochanteric prominence;
- Knee – bilateral, at the medial fat pad proximal to the joint line;
Digital palpation should be performed with an approximate force of 4 kg. For a tender point to be considered "positive" the subject must state that the palpation was painful. "Tender" is not to be considered "painful." For classification purposes, patients will be said to have fibromyalgia if both criteria are satisfied. Widespread pain must have been present for at least 3 months. The presence of a second clinical disorder does not exclude the diagnosis of fibromyalgia.
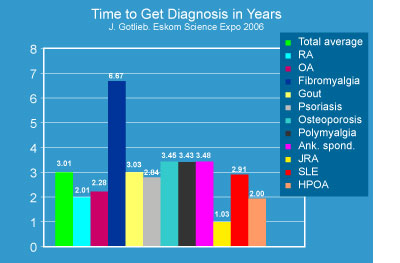
Diagnosis of fibromyalgia is difficult. It is estimated that it takes more than five years from first symptoms to the final diagnosis in the USA.
The figure shows average time needed to get diagnosis of different diseases with joint pain. Abbreviations: RA - rheumatoid arthritis, AO - osteoarthritis, Ank. spond. - ankylosing spondylitis, JRA - juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, SLE - systemic lupus erythematosus, HPOA - hypertrophic osteoarthropaty. Click to figure to get it magnified.
Here you may download a form with new diagnostic criteria for
fibromyalgia → diagnostic questionnaire
This form is an interactive pdf file and may help you to find out
if the fibromyalgia might be responsible for your symptoms.
It helps to calculate value of Widespread Pain Index (WPI) and Symptoms Severity score (SS score). The questionnaire has built-in sending function that could be executed if your computer has an active internet connection. You may send your questionnaire to our medical consultant if you want to get his opinion. Your pesonal data will be treated according to our privacy policy!
Please Notice: The filled up questionnaire should be saved to your own computer under its new unique file name before sending! Otherwise your data might lost or document could be mistaken with another one having identical name.
Important! The questionnaire does not substitute diagnosis made by experienced physician. The patient should not diagnose himself or herself. Patient should always consult his/her doctor in order to establish diagnosis and treatment plan. This questionnaire should give you insight in new clinical fibromyalgia diagnostic criteria.